NASA Announces Live Stream of International Space Station Resupply Mission
Updated: 2023-11-30 20:04:01
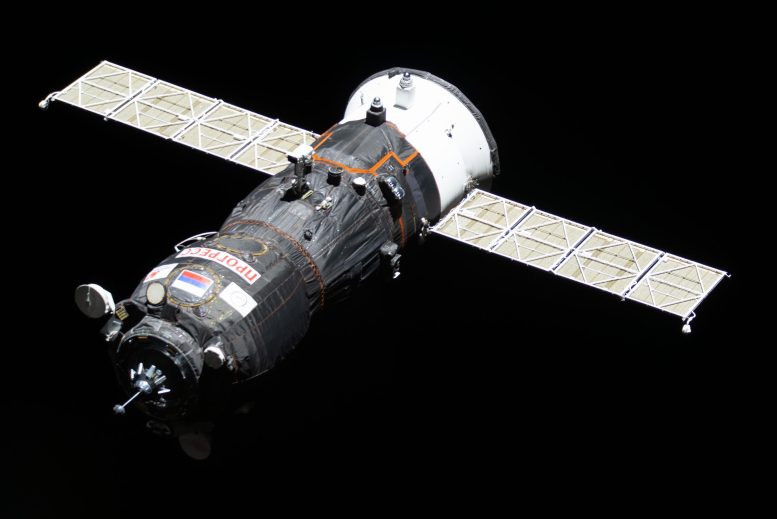 NASA will provide live launch and docking coverage of the Roscosmos Progress 86 cargo spacecraft carrying about three tons of food, fuel, and supplies for...
NASA will provide live launch and docking coverage of the Roscosmos Progress 86 cargo spacecraft carrying about three tons of food, fuel, and supplies for...
 A pivotal study by scientists at the Institute of Modern Physics has uncovered molecular-type structures in atomic nuclei, revolutionizing our understanding of nuclear matter. Scientists...
A pivotal study by scientists at the Institute of Modern Physics has uncovered molecular-type structures in atomic nuclei, revolutionizing our understanding of nuclear matter. Scientists...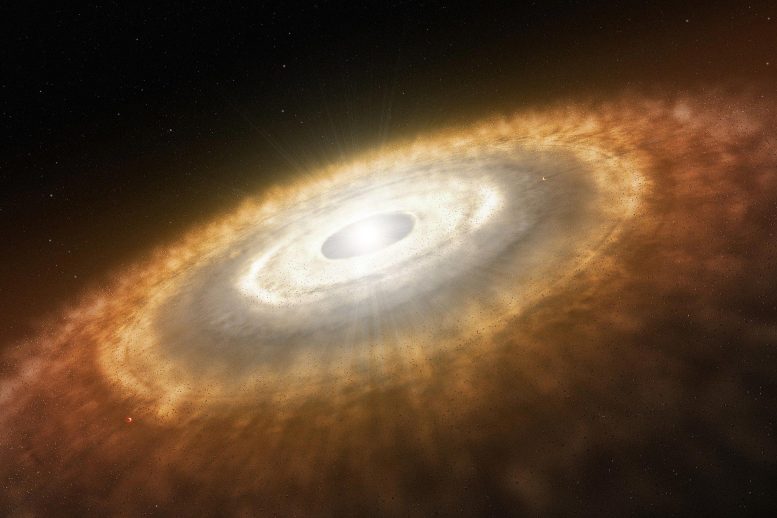 A groundbreaking discovery by astronomers reveals a rotating disk around a high-mass star in the Large Magellanic Cloud, offering new insights into star formation in...
A groundbreaking discovery by astronomers reveals a rotating disk around a high-mass star in the Large Magellanic Cloud, offering new insights into star formation in... In the era of big data and advanced artificial intelligence, traditional data storage methods are becoming inadequate. To address the need for high-capacity and energy-efficient...
In the era of big data and advanced artificial intelligence, traditional data storage methods are becoming inadequate. To address the need for high-capacity and energy-efficient...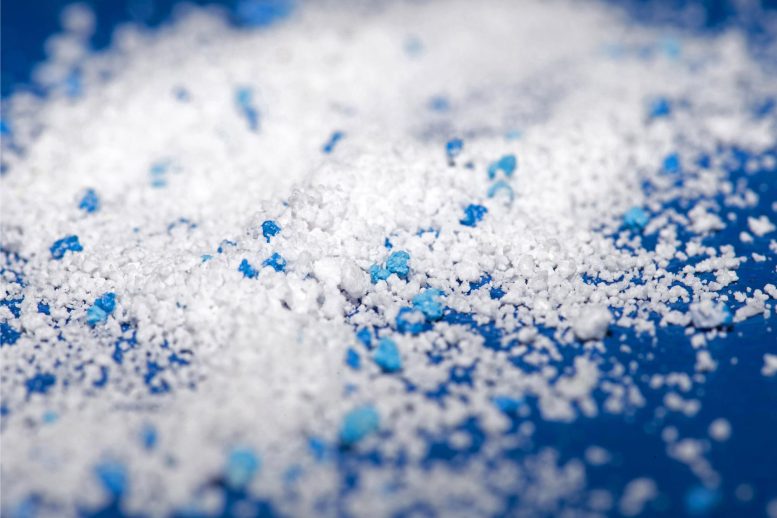 A new study quantifies how much microplastic is sent into the air from ocean spray. When sea bubbles pop, they launch tiny particles, like salt...
A new study quantifies how much microplastic is sent into the air from ocean spray. When sea bubbles pop, they launch tiny particles, like salt...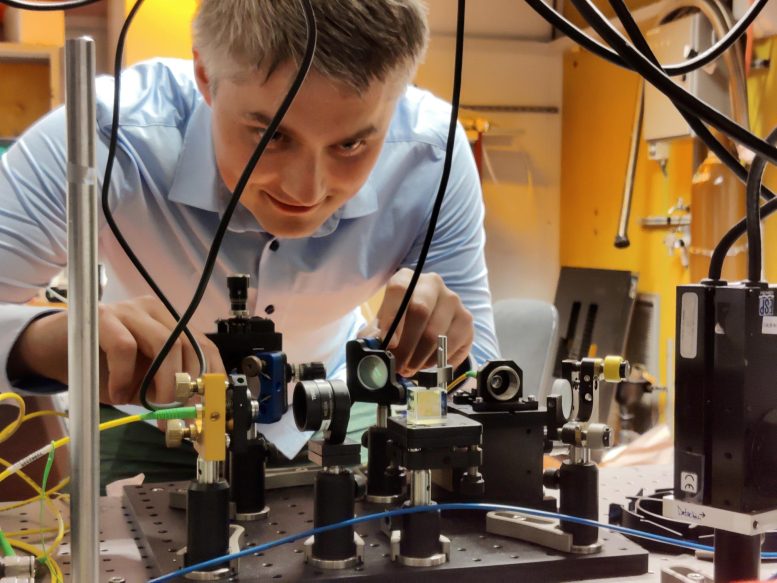 Petr Steindl creates complex structures of light using single photons. As a teenager, he wanted to study Czech poetry but decided on quantum physics after...
Petr Steindl creates complex structures of light using single photons. As a teenager, he wanted to study Czech poetry but decided on quantum physics after... Hubble Telescope confirms the size of Earth-like exoplanet LTT 1445Ac, offering new insights into its composition and the potential for further atmospheric study. Lots of...
Hubble Telescope confirms the size of Earth-like exoplanet LTT 1445Ac, offering new insights into its composition and the potential for further atmospheric study. Lots of...